- Science
- Clinical Trials
- Guide to Clinical Trials Your participation makes a difference
- Clinical Trials in Children Designed to improve kids' health
- Data and Results Sharing our Results
- Integrity and Transparency Building Trust
- Diversity Equity and Representation
- Plain Language Study Results Trial Result Summaries
- Expanded Access & Compassionate Use Possible Treatment Options
- Find a Trial
- Areas of Focus
- Rare Disease Smaller populations but big impact
- Internal Medicine Extending lifespans worldwide
- Inflammation & Immunology Treatment at the molecular level
- Vaccines Preventing the spread of infections
- Oncology The science of optimism
- Anti Infectives Combatting an evolving risk
- Areas of Innovation
- Gene Therapy Breakthroughs become treatments
- Medicinal Sciences The next generation of science
- Precision Medicine Developing tailored medicines
- Maternal Immunization Protecting newborns at the start
- mRNA Technology Unleashing the next wave of scientific innovations
- Diseases & Conditions
- Coronavirus Resources
- Product Pipeline
- Research Sites
- Clinical Trials
- Products
- How Drugs are Made
- Branded vs. Generic Learn the difference
- Biologics & Biosimilars Cures found in nature
- Commitment to Quality Maintaining the highest standards
- Global Supply Strategic manufacturing locations
- Manufacturing Sites Where medicine is made in the U.S.
- Medicine Safety
- Health Literacy Learning to be well
- Treatment Choices Learning about treatment decisions
- Partnering With Patients Helping others by reporting side effects
- Tips for Patients Preventing medication errors
- Reporting Adverse Events
- Counterfeiting Preventing medication errors
- Product Safety
- Product List
- Product Contacts
- PfizerPro for Professionals
- Patient Assistance Programs
- Distributors
- How Drugs are Made
- Stories
- Newsroom
- About
- People
- Executives Our senior-most leadership
- Board Members The people steering our company
- Scientists Our experts making discoveries
- Patient Stories Our patients
- Colleague Stories Our colleagues
- Responsibility
- Ethics & Compliance Each of us is responsible
- Responsible Business Breakthroughs that change patients’ lives
- Patient Advocacy & Engagement Putting Patients First
- Global Impact Meeting urgent needs worldwide
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Everyone has something to offer
- Environmental Sustainability Our responsiblity to the environment
- Human Rights Furthering dignity and worth
- Health & Safety
- Intellectual Property The benefits of fair competition
- EHS Governance
- Misinformation
- Programs & Policies
- Grants Support for independent research
- Political Partnership Supporting like-minded organizations
- Working with Healthcare Professionals Collaboration to improve lives
- Prescription Value & Pricing How to lower patient costs
- Privacy Principles Commitment to personal data privacy
- Ready for Cures Improving Access to Medicines
- Transparency in Grants Committed to Disclosure
- Policy Positions
- Investors
- Investors Overview Information for stockholders
- Why Invest Why to join us in our mission
- Events & Presentations Calendar of upcoming events
- Financial Reports Quarterly reports and more
- Investor News Announcements about our performance
- Stock Information Charts and data
- Shareholder Services Information on stock transactions
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance Overview Gaining insight into our performance
- Board Committees & Charters Defining the corporate structure
- The Pfizer Board Policies Ensuring ethical leadership
- Corporate Governance FAQs Learn more about our approach
- Contact Our Directors Email any of our Directors
- Purpose
- History
- Careers
- Partners
- People
Our Pipeline:
Potential Breakthroughs in the Making
We're in relentless pursuit of medicines and vaccines that will benefit patients around the world. Our ambitions are big and our product pipeline has never been stronger.
Adjust filters or
to view products
Explore the Product Pipeline
Take a deep dive into the investigational medicines and vaccines we’re working on.
Updated as of October 29, 2024.
- Phase 1
- Phase 2
- Phase 3
- Registration
- Phase 1
- Phase 2
- Phase 3
- Registration
Discover
Filter
Search
Learn
End Tutorial
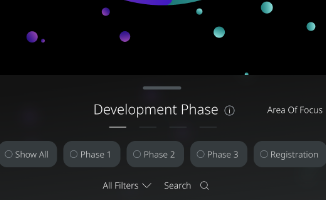
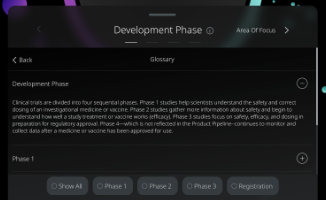
Development Phase
Back
Glossary
Development Phase
Clinical trials are divided into four sequential phases.
Phase 1 studies help scientists understand the safety and correct dosing of an investigational medicine or vaccine.
Phase 2 studies gather more information about safety and begin to understand how well a study treatment or vaccine works (efficacy).
Phase 3 studies focus on safety, efficacy, and dosing in preparation for regulatory approval. Phase 4—which is not reflected in the Product Pipeline--continues to monitor and collect data after a medicine or vaccine has been approved for use.
Phase 1
Phase 1 asks the questions “Is an investigational drug or vaccine safe?” and “What is the correct dose?” Typically, these studies are done with a small group of healthy volunteers.
But for some investigational therapies, such as those for cancer, the study is done with patients who have the condition the drug is targeted to treat.
In this stage, somewhat limited information is available about an investigational drug or vaccine. Scientists may still be gathering information about which specific disease to target with the investigational medicine.
Industry-wide, only 10% of Phase 1 candidates will make it to approval. On average, it takes 10 years to move from Phase 1 to regulatory approval.
Phase 2
Phase 2 asks the questions “Does this investigational medicine or vaccine work in the disease that’s targeted?” and “Are there any side effects that may occur?” These studies are done with a larger group of people—as many as several hundred participants—who have the condition the drug or vaccine is intended to treat. These studies last several months to a few years.
Phase 2 is often considered the steepest hurdle in clinical development. Some 70% of Phase 2 candidates industry-wide fail in this stage.
Phase 3
Phase 3 studies ask “How safe and effective the investigational drug or vaccine is for people with the condition and also sees if it works compared to a placebo or what else is currently available. Phase 3 studies seek to find out how safe and effective the investigational drug or vaccine is for people with the condition, and also if it works compared to a placebo or something else currently available. This phase usually signifies when an investigational medicine or vaccine may be two to three years from approval, subject to clinical trial and regulatory success.
Registration
After Phase 3, if the clinical trial data supports it, an extensive data package is submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and other regulatory authorities for review. This review process typically takes a year.
Show All
Phase 1
Phase 2
Phase 3
Registration
Area Of Focus
Back
Glossary
Area Of Focus
Our key areas of research, bucketed by disease type, biology area, or therapy type.
Anti-Infectives
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that target infectious diseases, which continue to be one of the biggest public health concerns around the world. Since our pioneering work on penicillin in the 1940s, we have a strong history of addressing this evolving risk.
Inflammation & Immunology
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that target chronic inflammatory diseases by treating them at the molecular level, and not just by relieving symptoms.
Internal Medicine
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that target cardiovascular (heart) and metabolic diseases, which are the number one cause of death worldwide. The development of these potential therapies aim to treat or prevent disease progression and improve the quality of life for patients.
Oncology
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that target cancer.
Vaccines
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that can stop a virus or bacterium before it can infect someone. Vaccines can give your body ways to identify an infecting agent, and instructions on how to defeat it—and potentially, to avoid infecting others.
Show All
Anti-Infectives
Inflammation & Immunology
Internal Medicine
Oncology
Vaccines
Submission Type
Back
Glossary
Submission Type
The FDA, the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other regulatory agencies around the globe have different application requirements depending on the type of investigational medicine or vaccine.
New Molecular Entity
A novel compound that has never been approved by a pharmaceutical regulatory agency (e.g., the FDA).
Product Enhancement
An approved or investigational drug that is being tested to potentially treat another related condition. For example, drugs approved for the treatment of one type of cancer may be tested to see if they are potentially effective across another type of cancer.
Show All
New Molecular Entity
Product Enhancement
Compound Type
Back
Glossary
Compound Type
The types of medicines that we’re currently developing.
Biologic
A type of medicine made from biological sources, such as living cells. Some of the more well-known biologics treat autoimmune conditions.
Small Molecule
Medicines made from chemical compounds and manufactured by chemical synthesis. These are generally in pill form.
Vaccine
A biological substance that stimulates an immune response against a disease. They’re usually given by injections.
Show All
Biologic
Small Molecule
Vaccine
Project Status
Back
Glossary
Project Status
Designation of whether a project is “current” or “discontinued.”
Current
An investigational drug or vaccine that is currently being evaluated in clinical trials.
Discontinued
When an investigational drug or vaccine shows an unacceptable safety/tolerability profile or lack of efficacy, or for other reasons, the clinical development program can be stopped. This entry will then be removed from the pipeline.
Project Advanced
A designation of 'Project Advanced' reflects a current candidate that has progressed from one Phase of Development to another, or has entered Phase 1, since the last pipeline update.
Show All
Current
Discontinued
Project Advanced
Indications
Back
Glossary
Fast Track
Fast Track (U.S.) is a designation available to a product if it is intended, whether alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and it demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for such a disease or condition. This designation is intended to facilitate development and expedite review of drugs to treat serious and life-threatening conditions so that an approved product can reach the market expeditiously. More information about the qualifying criteria and features of the Fast Track program can be found on the FDA’s website.
Breakthrough Designation
Breakthrough Designation (U.S.) may be granted to a drug (alone or in combination with 1 or more other drugs) intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. A drug that receives breakthrough designation is eligible for all fast-track designation features and an FDA commitment to work closely with the sponsor to ensure an efficient drug development program. More information about the qualifying criteria and features of the Breakthrough program can be found on the FDA’s website.
Orphan Drug
Orphan Drug (U.S.) - Orphan drug status may be granted to drugs and biologics that are intended for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of rare diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the U.S., or that affect more than 200,000 persons but where it is unlikely that expected sales of the product would cover the sponsor’s investment in its development. More information about the qualifying criteria, features, and incentives involved in an orphan drug designation can be found on the FDA’s website.
Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT)
Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) (U.S.) is a designation that is granted to regenerative medicine therapies intended to treat, modify, reverse, or cure a serious condition, for which preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the medicine has the potential to address an unmet medical need. The RMAT designation includes all the benefits of the fast track and breakthrough therapy designation programs, including early interactions with FDA.
Rare Pediatric Disease (RPD)
Rare Pediatric Disease (RPD) (U.S.) designation may be granted to a drug intended to treat a rare pediatric disease that is serious or life-threatening in which the serious or life-threatening manifestations primarily affect patients from birth to 18 years, including neonates, infants, children, and adolescents.
Priority Review
Priority Review (U.S.) A U.S. drug application will receive a priority review designation if it is for a drug that treats a serious condition and, if approved, would provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness. A priority designation is intended to direct overall attention and resources to the evaluation of such applications. A priority review designation means that FDA’s goal is to act on the marketing application within 6 months of receipt (compared with 10 months under standard review). More information about the qualifying criteria and features of a priority review designation can be found on the FDA’s website.
Orphan Drug (E.U.)
Orphan Drug (E.U.) - Orphan drug status may be granted to drugs and biologics that are intended for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a life-threatening or chronically debilitating condition affecting no more than 5 in 10,000 persons in the European Union at the time of submission of the designation application, or that affect more than 5 in 10,000 persons but where it is unlikely that expected sales of the product would cover the investment in its development. More information about the qualifying criteria, features, and incentives involved in an orphan drug designation can be found on the EMA’s website.
PRIME
PRIME (E.U.) - The PRIME scheme is applicable to products under development which are innovative and yet to be placed on the EU market. The scheme aims to support medicinal products of major public health interest and from the viewpoint of therapeutic innovation. Medicines eligible for PRIME must address an unmet medical need, i.e., for which there exists no satisfactory method of diagnosis, prevention or treatment in the Community or, if such a method exists, in relation to which the medicinal product concerned will be of major therapeutic advantage to those affected. A product eligible for PRIME should demonstrate the potential to address, to a significant extent, the unmet medical need, for example by introducing new methods of therapy or improving existing ones. Data available to support the request for eligibility should support the claim to address the unmet medical need through a clinically meaningful improvement of efficacy, such as having an impact on the prevention, onset or duration of the condition, or improving the morbidity or mortality of the disease. EMA will provide early and enhanced support to optimize the development of eligible medicines. Products granted PRIME support are anticipated to benefit from the Accelerated Assessment procedure. More information about the qualifying criteria and features of PRIME and Accelerated Assessment can be found on the EMA’s website.
Show All
Fast Track
Breakthrough Designation
Orphan Drug
Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT)
Rare Pediatric Disease (RPD)
Priority Review
Orphan Drug (E.U.)
PRIME
Compound Name
Back
Glossary
Compound Name
'Compound Name' refers to a chemical substance or molecule that is being investigated for its potential therapeutic effects, using an internal Pfizer compound number, brand name and/or generic name.
Show All
All Filters
Search
Back
All Filters
Reset
Development Phase
Phase 1
Phase 2
Phase 3
Registration
Area Of Focus
Anti-Infectives
Inflammation & Immunology
Internal Medicine
Oncology
Vaccines
Submission Type
New Molecular Entity
Product Enhancement
Compound Type
Biologic
Small Molecule
Vaccine
Project Status
Current
Discontinued
Project Advanced
Back
Search Products
Back
result found
Development Phase
- Phase 1
- Phase 2
- Phase 3
- Registration
Area of focus
Submission Type
Compound Type
Project Status
results found
Pipeline
as of October 29, 2024
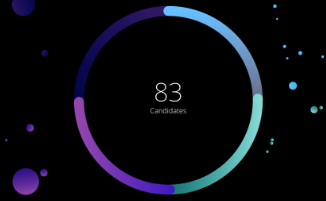
46
Phase 1
28
Phase 2
30
Phase 3
4
Registration
108
Total
Filters
Development Phase
Area Of Focus
Submission Type
Compound Type
Project Status
No Search Results Found!!
Adjust filters or
to view products
| COMPOUND NAME | INDICATION | AREA OF FOCUS | SUBMISSION TYPE | COMPOUND TYPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Phase 1 |
ABRYSVO
current
| Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection (pediatric) | Vaccines | Product Enhancement | Vaccine |
Phase 1 |
atirmociclib (PF-07220060)
current
| 1L Metastatic Breast Cancer | Oncology | New Molecular Entity | Small Molecule |
Phase 1 |
CTB+AVP (PF-07612577)
current
| Complicated Urinary Tract Infections (cUTI), Including Pyelonephritis (FAST TRACK - U.S.) | Anti-Infectives | New Molecular Entity | Small Molecule |
Phase 1 |
danuglipron (PF-06882961)
current
| Chronic Weight Management | Internal Medicine | New Molecular Entity | Small Molecule |
Phase 1 |
danuglipron (PF-06882961)
current
| Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Internal Medicine | Product Enhancement | Small Molecule |
Phase 1 |
Dekavil
current
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (Biologic) | Inflammation & Immunology | New Molecular Entity | Biologic |
Phase 1 |
felmetatug vedotin (PF-08046048) (B7H4V)
current
| Advanced Solid Tumors (Biologic) | Oncology | New Molecular Entity | Biologic |
Phase 1 |
PADCEV (enfortumab vedotin)
current
| BCG-Unresponsive Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (Biologic) | Oncology | Product Enhancement | Biologic |
Phase 1 |
PF-06835375
current
| Lupus (Biologic) | Inflammation & Immunology | Product Enhancement | Biologic |
Phase 1 |
PF-06940434
current
| Advanced Solid Tumors (Biologic) | Oncology | New Molecular Entity | Biologic |
Glossary
Development Phase
Clinical trials are divided into four sequential phases.
Phase 1 studies help scientists understand the safety and correct dosing of an investigational medicine or vaccine.
Phase 2 studies gather more information about safety and begin to understand how well a study treatment or vaccine works (efficacy).
Phase 3 studies focus on safety, efficacy, and dosing in preparation for regulatory approval. Phase 4—which is not reflected in the Product Pipeline--continues to monitor and collect data after a medicine or vaccine has been approved for use.
Phase 1
Phase 1 asks the questions “Is an investigational drug or vaccine safe?” and “What is the correct dose?” Typically, these studies are done with a small group of healthy volunteers.
But for some investigational therapies, such as those for cancer, the study is done with patients who have the condition the drug is targeted to treat.
In this stage, somewhat limited information is available about an investigational drug or vaccine. Scientists may still be gathering information about which specific disease to target with the investigational medicine.
Industry-wide, only 10% of Phase 1 candidates will make it to approval. On average, it takes 10 years to move from Phase 1 to regulatory approval.
Phase 2
Phase 2 asks the questions “Does this investigational medicine or vaccine work in the disease that’s targeted?” and “Are there any side effects that may occur?” These studies are done with a larger group of people—as many as several hundred participants—who have the condition the drug or vaccine is intended to treat. These studies last several months to a few years.
Phase 2 is often considered the steepest hurdle in clinical development. Some 70% of Phase 2 candidates industry-wide fail in this stage.
Phase 3
Phase 3 studies ask “How safe and effective the investigational drug or vaccine is for people with the condition and also sees if it works compared to a placebo or what else is currently available. Phase 3 studies seek to find out how safe and effective the investigational drug or vaccine is for people with the condition, and also if it works compared to a placebo or something else currently available. This phase usually signifies when an investigational medicine or vaccine may be two to three years from approval, subject to clinical trial and regulatory success.
Registration
After Phase 3, if the clinical trial data supports it, an extensive data package is submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and other regulatory authorities for review. This review process typically takes a year.
Area Of Focus
Our key areas of research, bucketed by disease type, biology area, or therapy type.
Anti-Infectives
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that target infectious diseases, which continue to be one of the biggest public health concerns around the world. Since our pioneering work on penicillin in the 1940s, we have a strong history of addressing this evolving risk.
Inflammation & Immunology
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that target chronic inflammatory diseases by treating them at the molecular level, and not just by relieving symptoms.
Internal Medicine
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that target cardiovascular (heart) and metabolic diseases, which are the number one cause of death worldwide. The development of these potential therapies aim to treat or prevent disease progression and improve the quality of life for patients.
Oncology
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that target cancer.
Vaccines
This Area of Focus specializes in therapies that can stop a virus or bacterium before it can infect someone. Vaccines can give your body ways to identify an infecting agent, and instructions on how to defeat it—and potentially, to avoid infecting others.
Submission Type
The FDA, the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other regulatory agencies around the globe have different application requirements depending on the type of investigational medicine or vaccine.
New Molecular Entity
A novel compound that has never been approved by a pharmaceutical regulatory agency (e.g., the FDA).
Product Enhancement
An approved or investigational drug that is being tested to potentially treat another related condition. For example, drugs approved for the treatment of one type of cancer may be tested to see if they are potentially effective across another type of cancer.
Compound Type
The types of medicines that we’re currently developing.
Biologic
A type of medicine made from biological sources, such as living cells. Some of the more well-known biologics treat autoimmune conditions.
Small Molecule
Medicines made from chemical compounds and manufactured by chemical synthesis. These are generally in pill form.
Vaccine
A biological substance that stimulates an immune response against a disease. They’re usually given by injections.
Project Status
Designation of whether a project is “current” or “discontinued.”
Current
An investigational drug or vaccine that is currently being evaluated in clinical trials.
Discontinued
When an investigational drug or vaccine shows an unacceptable safety/tolerability profile or lack of efficacy, or for other reasons, the clinical development program can be stopped. This entry will then be removed from the pipeline.
Project Advanced
A designation of 'Project Advanced' reflects a current candidate that has progressed from one Phase of Development to another, or has entered Phase 1, since the last pipeline update.
Fast Track
Fast Track (U.S.) is a designation available to a product if it is intended, whether alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and it demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for such a disease or condition. This designation is intended to facilitate development and expedite review of drugs to treat serious and life-threatening conditions so that an approved product can reach the market expeditiously. More information about the qualifying criteria and features of the Fast Track program can be found on the FDA’s website.
Breakthrough Designation
Breakthrough Designation (U.S.) may be granted to a drug (alone or in combination with 1 or more other drugs) intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. A drug that receives breakthrough designation is eligible for all fast-track designation features and an FDA commitment to work closely with the sponsor to ensure an efficient drug development program. More information about the qualifying criteria and features of the Breakthrough program can be found on the FDA’s website.
Orphan Drug
Orphan Drug (U.S.) - Orphan drug status may be granted to drugs and biologics that are intended for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of rare diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the U.S., or that affect more than 200,000 persons but where it is unlikely that expected sales of the product would cover the sponsor’s investment in its development. More information about the qualifying criteria, features, and incentives involved in an orphan drug designation can be found on the FDA’s website.
Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT)
Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) (U.S.) is a designation that is granted to regenerative medicine therapies intended to treat, modify, reverse, or cure a serious condition, for which preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the medicine has the potential to address an unmet medical need. The RMAT designation includes all the benefits of the fast track and breakthrough therapy designation programs, including early interactions with FDA.
Rare Pediatric Disease (RPD)
Rare Pediatric Disease (RPD) (U.S.) designation may be granted to a drug intended to treat a rare pediatric disease that is serious or life-threatening in which the serious or life-threatening manifestations primarily affect patients from birth to 18 years, including neonates, infants, children, and adolescents.
Priority Review
Priority Review (U.S.) A U.S. drug application will receive a priority review designation if it is for a drug that treats a serious condition and, if approved, would provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness. A priority designation is intended to direct overall attention and resources to the evaluation of such applications. A priority review designation means that FDA’s goal is to act on the marketing application within 6 months of receipt (compared with 10 months under standard review). More information about the qualifying criteria and features of a priority review designation can be found on the FDA’s website.
Orphan Drug (E.U.)
Orphan Drug (E.U.) - Orphan drug status may be granted to drugs and biologics that are intended for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a life-threatening or chronically debilitating condition affecting no more than 5 in 10,000 persons in the European Union at the time of submission of the designation application, or that affect more than 5 in 10,000 persons but where it is unlikely that expected sales of the product would cover the investment in its development. More information about the qualifying criteria, features, and incentives involved in an orphan drug designation can be found on the EMA’s website.
PRIME
PRIME (E.U.) - The PRIME scheme is applicable to products under development which are innovative and yet to be placed on the EU market. The scheme aims to support medicinal products of major public health interest and from the viewpoint of therapeutic innovation. Medicines eligible for PRIME must address an unmet medical need, i.e., for which there exists no satisfactory method of diagnosis, prevention or treatment in the Community or, if such a method exists, in relation to which the medicinal product concerned will be of major therapeutic advantage to those affected. A product eligible for PRIME should demonstrate the potential to address, to a significant extent, the unmet medical need, for example by introducing new methods of therapy or improving existing ones. Data available to support the request for eligibility should support the claim to address the unmet medical need through a clinically meaningful improvement of efficacy, such as having an impact on the prevention, onset or duration of the condition, or improving the morbidity or mortality of the disease. EMA will provide early and enhanced support to optimize the development of eligible medicines. Products granted PRIME support are anticipated to benefit from the Accelerated Assessment procedure. More information about the qualifying criteria and features of PRIME and Accelerated Assessment can be found on the EMA’s website.
Compound Name
'Compound Name' refers to a chemical substance or molecule that is being investigated for its potential therapeutic effects, using an internal Pfizer compound number, brand name and/or generic name.